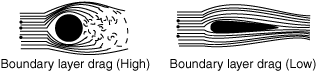
- boundary-layer normal-pressure drag
- A drag resulting from the shape of the body. Streamlining the exposed parts can reduce boundary-layer drag. See also form drag.
Aviation dictionary. 2014.

Aviation dictionary. 2014.
boundary-layer drag — A drag associated with losses of total pressure and total temperature in the boundary layers. It is the sum of the boundary layer normal pressure drag and the surface friction … Aviation dictionary
Boundary layer — For the anatomical structure, see Boundary layer of uterus. Boundary layer visualization, showing transition from laminar to turbulent condition In physics and fluid mechanics, a boundary layer is that layer of fluid in the immediate vicinity of… … Wikipedia
form drag — A type of parasitic drag. Form drag is caused by the frontal area of the airplane components being exposed to the airstream. Drag is caused by the form or shape of the body and, hence, the name. It can be reduced by streamlining the exposed parts … Aviation dictionary
Drag (physics) — Shape and flow Form drag Skin friction 0% 100% 10% 90% … Wikipedia
Aerodynamic drag — Note This article is currently under renovation, and may, at times, appear disjoint. Please see the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Talk:Aerodynamic drag Discussion Page] . Introduction Aerodynamic drag refers to the retarding force on moving… … Wikipedia
fluid mechanics — an applied science dealing with the basic principles of gaseous and liquid matter. Cf. fluid dynamics. [1940 45] * * * Study of the effects of forces and energy on liquids and gases. One branch of the field, hydrostatics, deals with fluids at… … Universalium
Lift (force) — For other uses, see Lift. Boeing 747 8F landing A fluid flowing past the surface of a body exerts a surface force on it. Lift is the component of this force that is perpendicular to the … Wikipedia
D'Alembert's paradox — In fluid dynamics, d Alembert s paradox (or the hydrodynamic paradox) is a contradiction reached in 1752 by French mathematician Jean le Rond d Alembert.[1] D Alembert proved that – for incompressible and inviscid potential flow – the drag force… … Wikipedia
climate — /kluy mit/, n. 1. the composite or generally prevailing weather conditions of a region, as temperature, air pressure, humidity, precipitation, sunshine, cloudiness, and winds, throughout the year, averaged over a series of years. 2. a region or… … Universalium
Wind tunnel — A wind tunnel is a research tool developed to assist with studying the effects of air moving over or around solid objects.Ways that wind speed and flow are measured in wind tunnels: * Threads can be attached to the surface of study objects to… … Wikipedia